Artificial intelligence is being developed to supply a robotic thoughts for a future NASA mission to land on the icy ground of certainly one of many photograph voltaic system’s ocean moons, equivalent to Europa or Enceladus.
The autonomous software program program is being developed by teams of researchers who’re making use of a robotic arm, mimicking that belonging to a lander or rover, and a digital actuality simulation at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and Ames Evaluation Coronary heart, respectively.
Take into consideration that you’re a robotic lander designed to assessment Jupiter‘s moon Europawhich hosts a deep water ocean far beneath its icy ground. You’ve got bought braved the radiation belts of the big planet, your retrorockets have fired and you’ve got safely touched down onto the ice. Apart from — possibly the terrain is further hazardous than you realized it was going to be, with large ice boulders or deep ravines. Maybe the properties of the ice listed beneath are fully totally different — extra sturdy, or thinner, or broken up by micrometeorite impacts.
You try and take a sample, nevertheless your scoop will get snagged on one factor, or your drill turns into jammed throughout the ice. You’ve got bought acquired a problem — and it might take as a lot as 53 minutes, relying upon the place Earth and Jupiter are of their respective orbits, sooner than your group once more on Earth is conscious of one thing about it, and at biggest one different 53 minutes, most probably longer, sooner than they ship you directions. By that time, your drill may want broken, in any other case you may want tumbled proper right into a ravine. How considerably higher in your survival would it not not be in case you could make some choices by your self?
Related: Watch this Jupiter moon lander cope with harsh terrain it’d face on Europa (video)
That’s what engineers and planetary scientists at NASA are hoping to realize with two agency-funded functions that goal to develop autonomous software program program, educated using machine finding outreasoning and generative artificial intelligence, for future lander and rover missions to the ocean moons.
These functions are the Ocean Worlds Lander Autonomy Testbed (OWLAT), which is a robotic setup at JPL, and the Ocean Worlds Autonomy Testbed for Exploration, Evaluation and Simulation (OceanWATERS), which is a purely virtual-reality system at NASA Ames
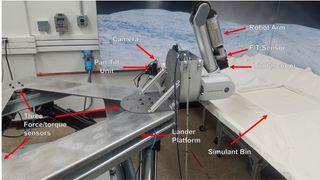
OWLAT sits throughout the nook of an office at JPL, solely a robotic arm on a check out bench in entrance of an artist’s mural of the rugged, frozen ground of an ocean moon. OWLAT is designed to bodily replicate how a robotic arm might perform throughout the low-gravity ambiance of one amongst these moons. With the arm, engineers can simulate scooping supplies off the ground, drilling or penetrating into the ice, along with measuring the ice’s properties through the use of a shear bevameter (which judges a ground’s functionality to take the load of a wheeled automotive on it) or a pressure sinkage plate (which measures how rather a lot the underside sinks when pressure is utilized).

The arm features a pan-and-tilt digital digicam to look at what the devices have accomplished, and seven ranges of freedom to allow the arm to hold out superior motions. Constructed-in drive and torque sensors measure the motion and response response of the arm, feeding it once more to the Robotic Working System. Researchers can simulate faults, technical failures and hazards to see how the arm’s autonomous software program program reacts to points without having assist from residence.
Within the meantime, OceanWATERs does the an identical issue, nevertheless in digital actuality and with a complete lander based on a 2016 design analysis, not solely a robotic arm. Numerous detailed terrain fashions could also be chosen for the simulation, not merely variations of icy moons, however as well as Earth’s Atacama Desert in Chile, which is usually used as a stand-in for a bleak ambiance. Due to OceanWATERS’ Generic Software program program Construction for Prognostics (GSAP) system, certainly one of many points that the simulation can model is battery vitality: how rather a lot vitality is consumed by the lander performing positive actions, and the way in which rather a lot life the battery has left in it.
Every OWLAT and OceanWATERs are based on the an identical Robotic Working System, which is autonomous software program program that receives telemetry from the robotic’s sensors and factors directions in response. By the use of the Robotic Working System, assorted mission goals could also be simulated, and fault-correction software program program based on A.I. can deal with points after they arrive up.
Fault recognition and prevention had been a key focus of present evaluation by six teams, all of which used OceanWATERS and three of which moreover involved OWLAT, with the intention of furthering the occasion of software program program which may sooner or later be used on a lander on an icy ocean moon for precise. As an illustration, they’d been able to reinforce decision-making software program program by teaching it with reinforcement finding out methods, develop automated planning {{that a}} lander could make use of to maximise the science it might probably do must communications with Earth be interrupted, and write software program program that is able to autonomously adapt must the terrain it lands on or digs into not be what was anticipated, requiring a degree of adaptation.
Related: Europa Clipper: An entire data to NASA’s astrobiology mission

There are a choice of huge, icy moons throughout the outer photograph voltaic systemand plenty of are thought to incorporate oceans, so there is no shortage of targets for a future lander to go to.
Presently, Europa and the Saturn satellite tv for pc television for computer Enceladus are the prime targets, primarily as a result of their potential to host lifetime of their oceans; at Saturnwhich is 1.4 billion kilometers (870 million miles) from the photo voltaicthe time lag is even worse. Nonetheless, the European Space Firm (ESA) effectively landed its Huygens probe on Saturn’s moon Titan in January 2005, so touchdowns on these distant, frigid moons are attainable.

NASA's Europa Clipper spacecraft is now on its answer to look at the eponymous Jovian moon, whereas ESA’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) may be en path to hold out two flybys of Europa along with conduct in-depth analysis of Europa’s fellow Galilean moons Ganymede and Callistofinally coming into into orbit spherical Ganymede.
Whereas neither Europa Clipper nor JUICE will land, their high-resolution exploration of these icy moons will give mission planners a considerably higher considered what to anticipate after they do come to launch a lander mission, and the place the right web sites to hunt for proof of life in these alien oceans is more likely to be. When these missions lastly do happen, they would be the neatest spacecraft ever launched, and their robotic IQ shall be traceable all the easiest way once more to a robotic arm in a lab, and a digital actuality simulation.














Leave a Reply